Chapter 1: Business Driven Technology
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY'S ROLE IN BUSINESS
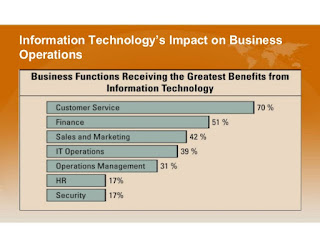
Information Technology's Impact on Business Operations
Information Technology Basics
- Information technology is everywhere in business
Information Technology's Impact on Business Operations
- Organizations typically operate by functional areas or functional silos
- Functional areas are interdependent
Information Technology Basics
- Information technology (IT) is a field concerned with the use of technology in managing and processing information
- Information technology is an important enabler of business success and innovation
- Information technology (IT) is the application of ccomputers to store, study, retrieve, transmit, and manipulate data or information, often in the context of a business or other enterprise.
- Management information systems (MIS) is a general name for the business function and academic discipline covering the application of people, technologies, and procedures to solve business problems
- MIS is a business function, similar to Accounting, Finance, Operations, and Human Resources
- When beginning to learn about information technology it is important to understand the data, information and business intellligence IT resources and IT cultures.
INFORMATION
- Data: raw facts that describe the characteristic of an event
- Information: Data cinverted into a meaningful and useful context
- Business intelligence: Applications and technologies that are used to support decion-making efforts
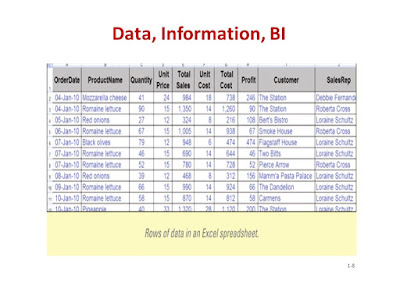
Example:
- DATA IN AN EXCEL SPREADSHEET
- DATA TURNED INTO INFORMATION
- INFORMATION TURNED INTO BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE
These multiple sources include:
- Suppliers → Customers
- Competitors → Business partner
- Data from industry → Data from governmental sources
IT RESOURCES
IT CULTURES
- Organizational information cultures include:
- Information-Functional Culture - all employees use information as a means of exercising influence or power over others. For explample, a manager is sales refuses to share inforamtion with marketing. This cause marketing to need the sales manager's input each time a new sales strategy is developed
- Information-Sharing Culture - all employees across departments trust each other to use information ( especially about problems and failures) to improve perfomrance.
- Information-Inquiring Culture - all employees across departments search for information to better understand with current trends and new directions.
- Information- all employess across departments are open to new sights about crisis and radical changes and seek ways to create competitive advanatges.





Comments
Post a Comment